Chapter 4.4 - Retrain the model from new data with DVC¶
Introduction¶
In this chapter, we will retrain the model using the new data we labeled in the previous chapter. We will download the annotations from Label Studio and use them to retrain the model. We will then evaluate the new model to see if it has improved.
The following diagram illustrates the control flow of the experiment at the end of this chapter:
flowchart TB
extra_data -->|upload| labelStudioTasks
labelStudioTasks -->|label| labelStudioAnnotations
bento_model -->|load| fastapi
labelStudioTasks -->|POST /predict| fastapi
fastapi --> labelStudioPredictions
labelStudioPredictions -->|submit| labelStudioAnnotations
labelStudioAnnotations -->|download| extra_data_annotations
extra_data_annotations --> |load| parse_annotations
parse_annotations -->|copy| data_raw
data_raw -->|dvc repro| bento_model
subgraph workspaceGraph[WORKSPACE]
extra_data[extra-data/extra_data]
extra_data_annotations[extra-data/extra_data/annotations.json]
bento_model[model/classifier.bentomodel]
fastapi[src/serve_label_studio.py]
parse_annotations[scripts/parse_annotations.py]
data_raw[data/raw]
end
subgraph labelStudioGraph[LABEL STUDIO]
labelStudioTasks[Tasks]
labelStudioAnnotations[Annotations]
labelStudioPredictions[Predictions]
end
style extra_data opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
style labelStudioTasks opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
style fastapi opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
style labelStudioPredictions opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 0 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 1 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 2 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 3 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 4 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 5 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80Steps¶
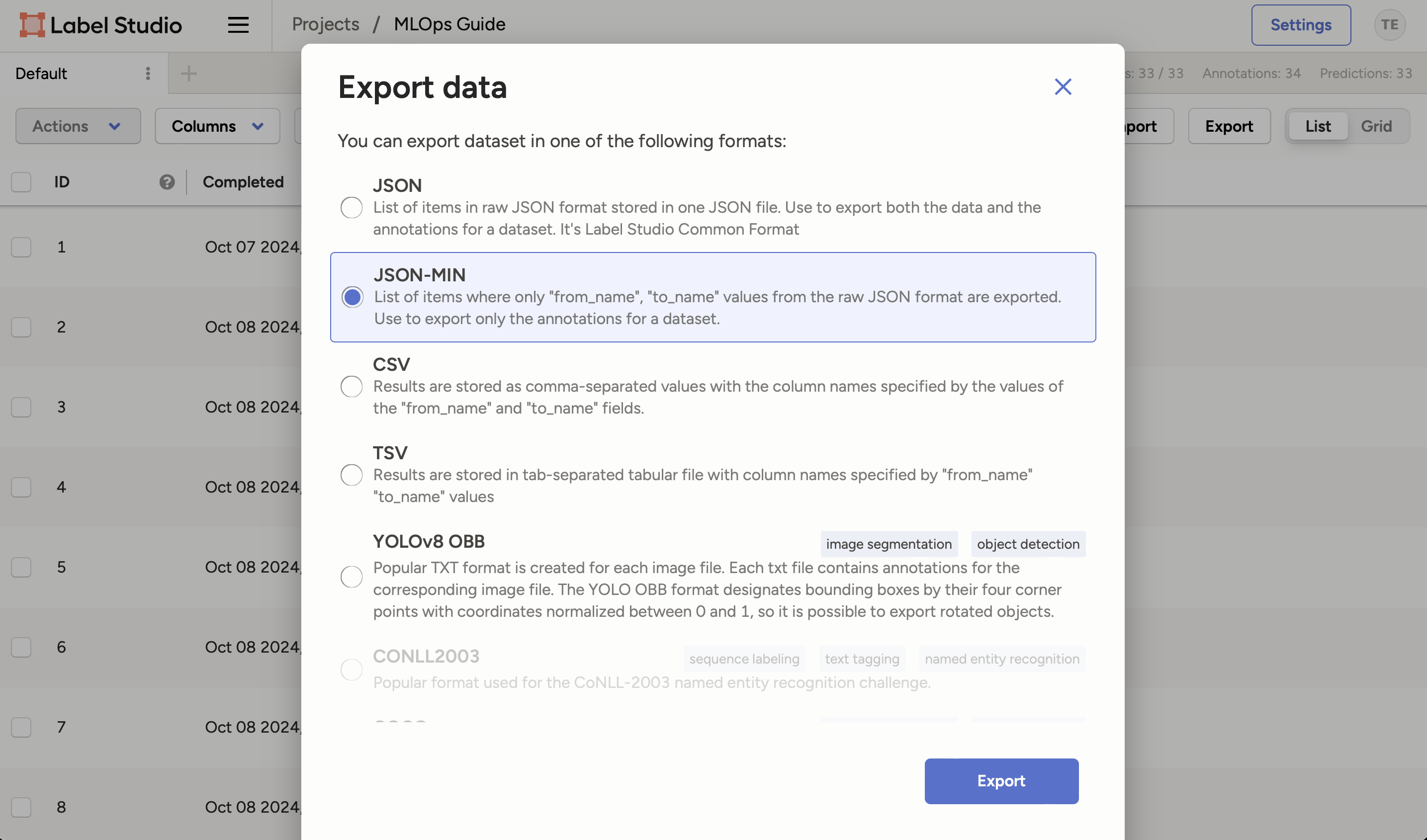
Download the annotations¶
Make sure Label Studio is running at http://localhost:8080.
-
In the project view, click on the Export button and select
JSON-MINI. -
Click on the Export button to download the annotations.
-
Rename the downloaded json file to
annotations.json. -
Move the file to your
a-guide-to-mlopsrepository under theextra-data/folder.- This is the annotations file we downloaded from Label Studio.
Parse the annotations¶
Label Studio exports the annotations in a specific format. We need to parse these annotations to extract the labels and the corresponding data.
For this, we will use a Python script. Create a new Python script called parse_annotations.py in a new scripts/ folder of your repository.
The script reads the annotations from the annotations.json file and copies the images to the corresponding folders in the data/raw directory.
You can run the script using the following command:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
The annotated images will be copied to the data/raw directory. The output should look like this:
Check the changes¶
Check the changes with Git to ensure that all the necessary files are tracked:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
The output should look like this:
Commit the changes to Git¶
Commit the changes to Git:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
Retrain the model¶
Now that we have the new data, we can retrain the model. We will use DVC:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
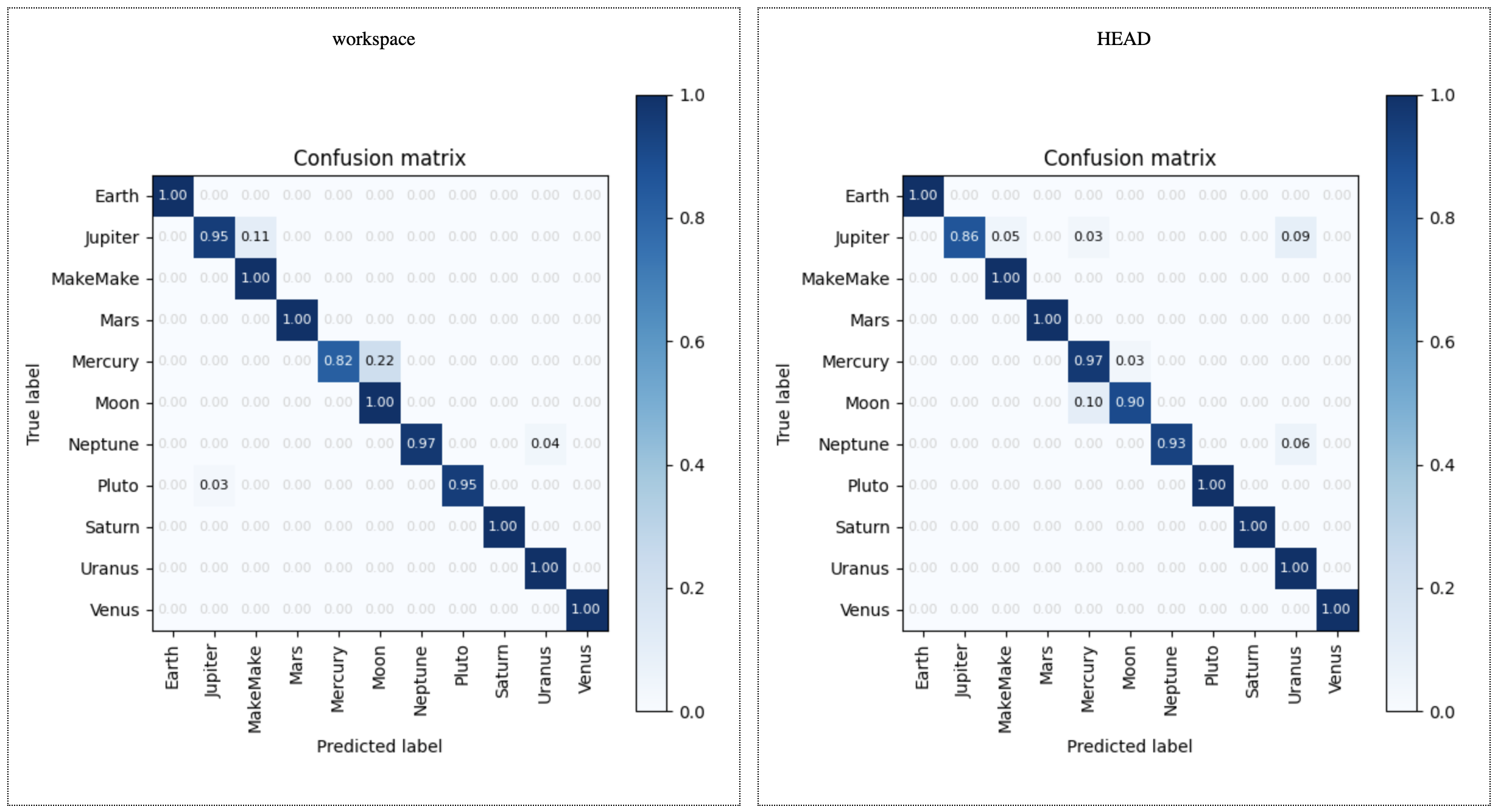
And check the new model's performance:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
The plot shows the performance of the old (right) and new model (left). You can see if the new model has improved.
Commit and push the updated data¶
Once you want to share the new data, commit the changes and push to DVC and Git:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
Summary¶
In this chapter, we retrained the model using the new data we labeled in Label Studio. We downloaded the annotations, parsed them, and retrained the model using DVC. We then evaluated the new model to see if it has improved.
State of the labeling process¶
- Labeling of supplemental data can be done systematically and uniformly
- Labeling of supplemental data is accelerated with AI assistance
- Model is retrained with the supplemental data