Chapter 4.3 - Link the model to Label Studio¶
Introduction¶
In this chapter, you will begin by creating an API for the model. Next, you will link the model you trained in the previous chapters to Label Studio using this API. This integration will enable the model to make predictions on the unlabeled data within Label Studio, rendering the labeling process "AI assisted" and thus making it significantly more efficient.
The following diagram illustrates the control flow of the experiment at the end of this chapter:
flowchart TB
extra_data -->|upload| labelStudioTasks
labelStudioTasks -->|label| labelStudioAnnotations
bento_model -->|load| fastapi
labelStudioTasks -->|POST /predict| fastapi
fastapi --> labelStudioPredictions
labelStudioPredictions -->|submit| labelStudioAnnotations
subgraph workspaceGraph[WORKSPACE]
extra_data[extra-data/extra_data]
bento_model[model/classifier.bentomodel]
fastapi[src/serve_label_studio.py]
end
subgraph labelStudioGraph[LABEL STUDIO]
labelStudioTasks[Tasks]
labelStudioAnnotations[Annotations]
labelStudioPredictions[Predictions]
end
style extra_data opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
style labelStudioTasks opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 0 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80
linkStyle 1 opacity:0.4,color:#7f7f7f80Steps¶
Install FastAPI¶
Before adding the model to Label Studio, we need to create an API for the model. Python has many packages for building web frameworks. In this guide we will use FastAPI for it's simplicity. Add the main fastapi[standard] dependency to the requirements.txt file:
| requirements.txt | |
|---|---|
Check the differences with Git to validate the changes:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
The output should be similar to this:
Install the package and update the freeze file.
Warning
Prior to running any pip commands, it is crucial to ensure the virtual environment is activated to avoid potential conflicts with system-wide Python packages.
To check its status, simply run pip -V. If the virtual environment is active, the output will show the path to the virtual environment's Python executable. If it is not, you can activate it with source .venv/bin/activate.
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
Create the model API¶
Let's start building the API which will allow Label Studio to talk with our model. Label Studio expects the following API endpoints:
- GET
/health- To check if the model is running. - POST
/setup- To configure the model API. It is useful if we have multiple models and we want to pick the right one for the task. - POST
/webhook- To start jobs such as model training from the Label Studio UI to our API. - POST
/predict- To make predictions using the model.
Let's implement these endpoints.
Create a new file src/serve_label_studio.py and add the following code:
This file is structured in 3 parts:
- Definition of some useful constants.
- Creation of the FastAPI app and loads the model similarly to BentoML
src/serve.py. - Definition the API endpoints required by Label Studio.
Note
We do nothing with the /setup and /webhook endpoints as we do not need the functionality they offer. However, they are still required to exist for the model to work with Label Studio. If you would like to go further, please refer the Label Studio ML integration documentation.
Check the changes¶
Check the changes with Git to ensure that all the necessary files are tracked:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
The output should look like this:
Commit the changes to Git¶
Commit the changes to Git:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
Run the model API¶
Run the model API by executing the following command:
| Execute the following command(s) in a terminal | |
|---|---|
The FastAPI server will start at http://localhost:8000 and you can view the documentation at http://localhost:8000/docs.
Make sure to keep the server running in the background for the next steps.
Add the model to Label Studio¶
Make sure Label Studio is running at http://localhost:8080.
-
Click on the Settings button on the top right corner of the screen and select Model from the sidebar.
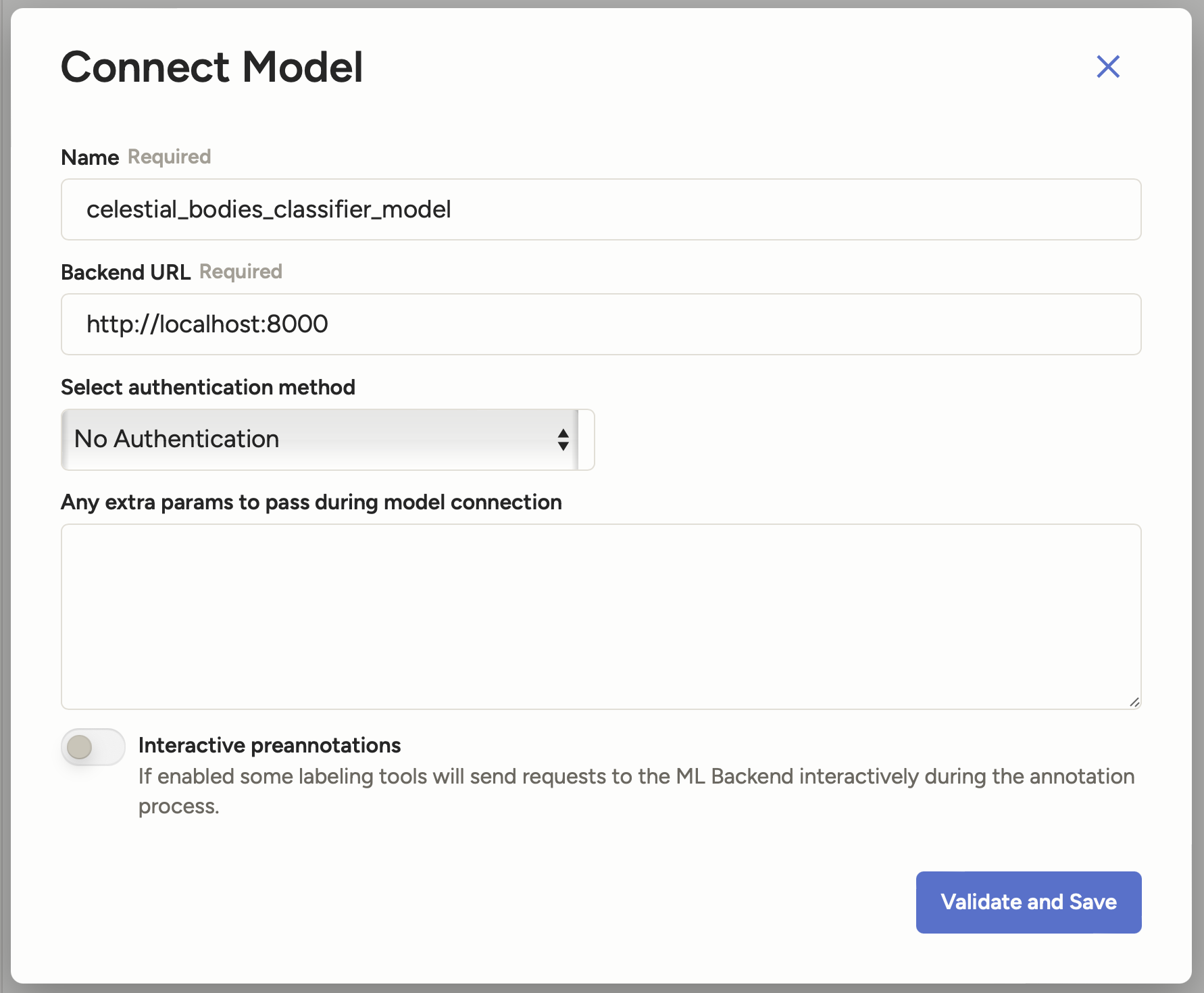
-
Click on the Connect Model button and enter the following details:
- Name:
celestial_bodies_classifier_model - Backend URL:
http://localhost:8000
It should look like this:
- Name:
-
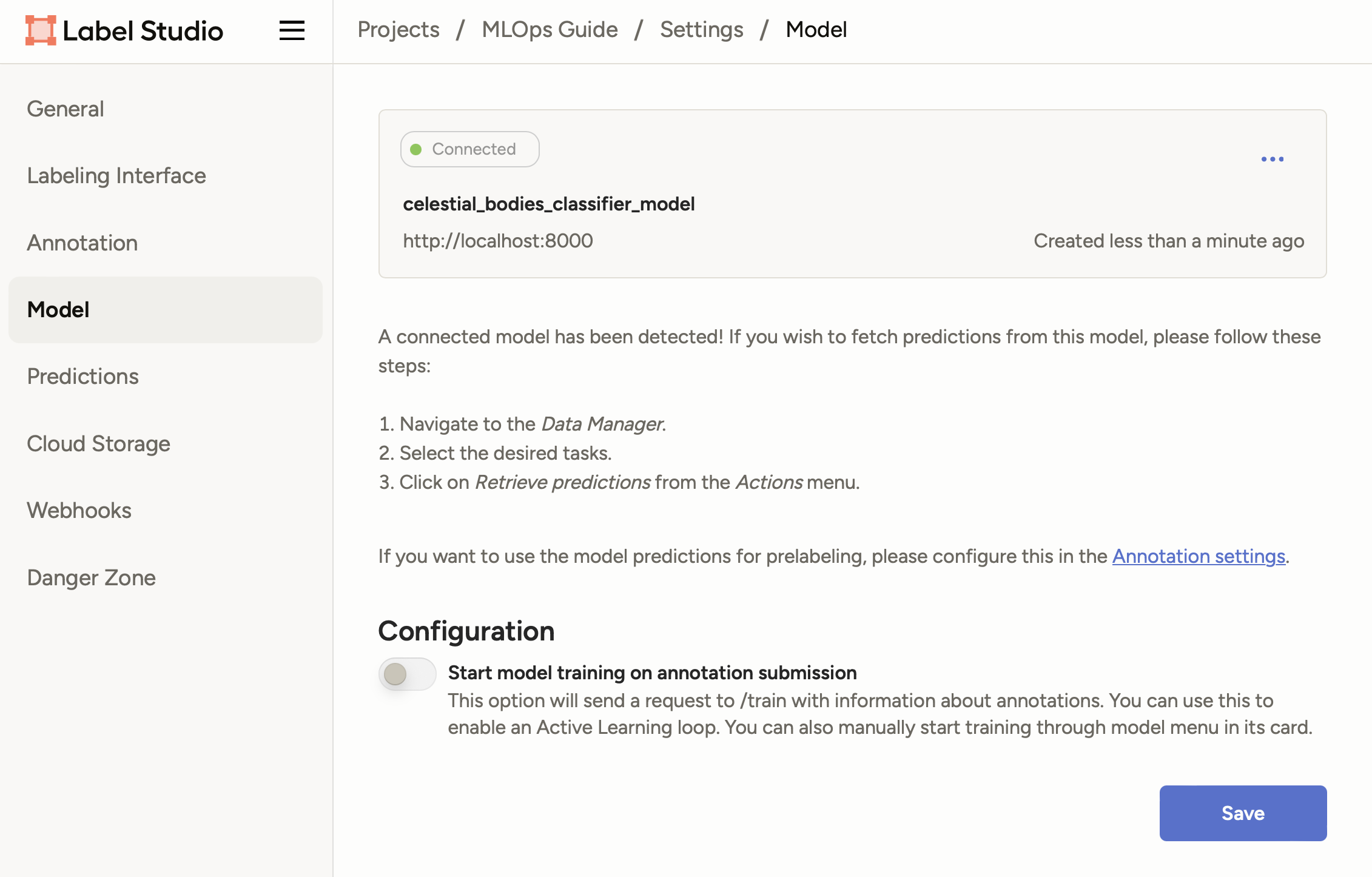
Click on Validate and Save to add the model.
You should now see your model with a status of Connected:
Label with the model¶
Now that the model is connected, you can start labeling the data.
-
Click on your project name on the top navigation bar to go back to the project view.
-
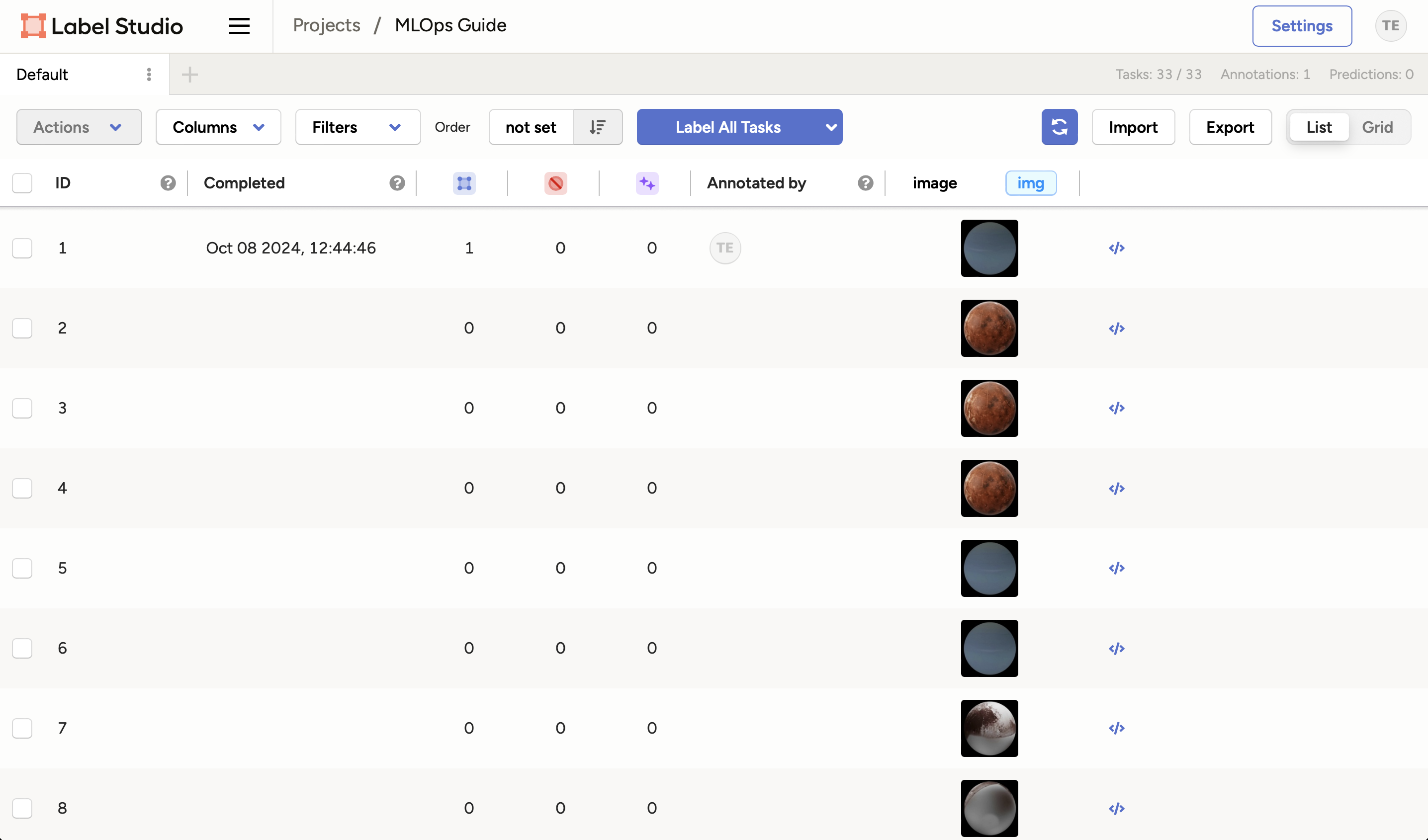
Click on the Label All Tasks button to start labeling the data. This will resume the labeling process from where you left off.
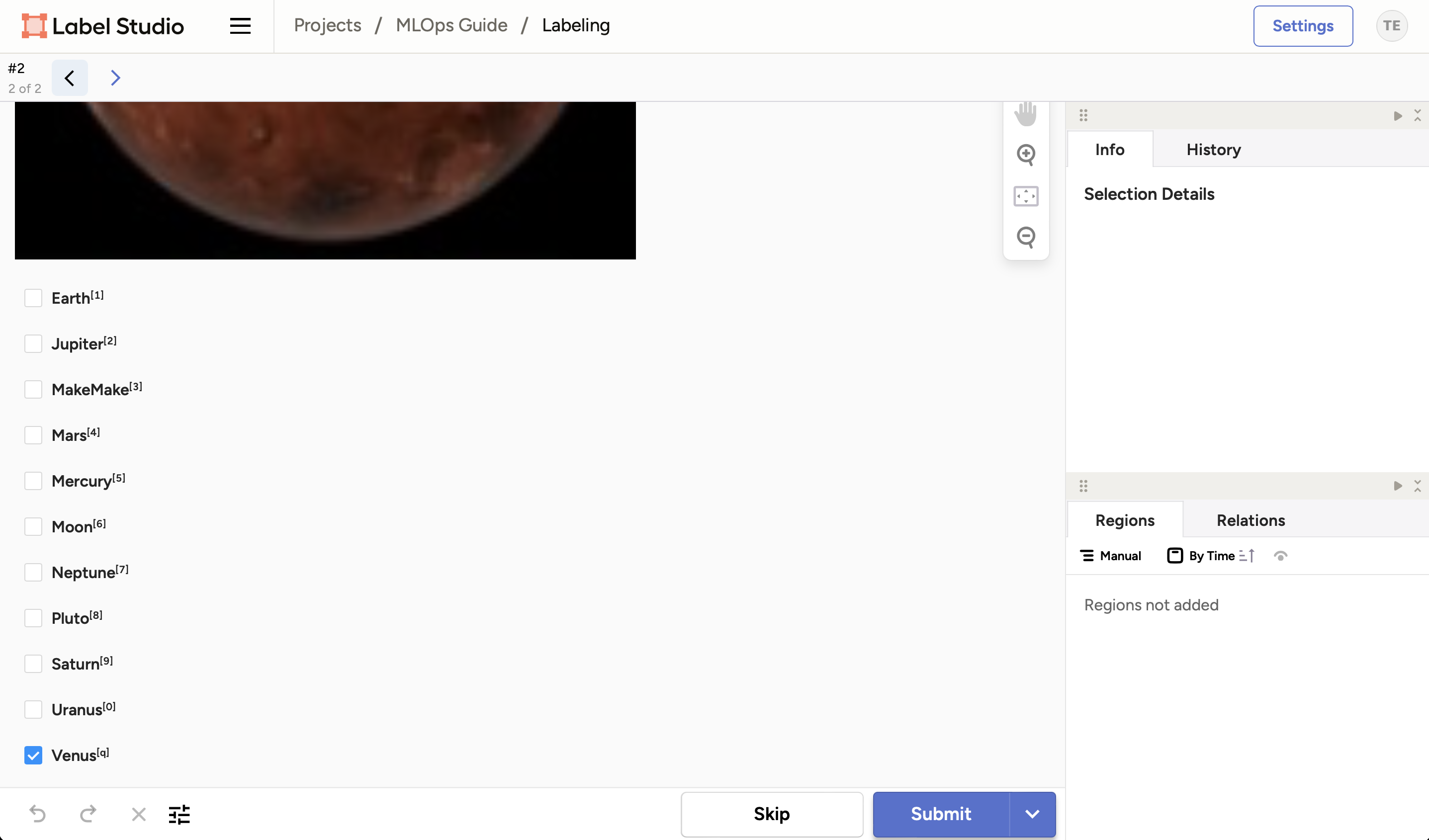
You should now see the image has been labeled automatically by the model:
-
Review the prediction and make any necessary corrections.
-
Click on the Submit button to save the annotation.
-
Continue labeling the data until you have labeled all the images.
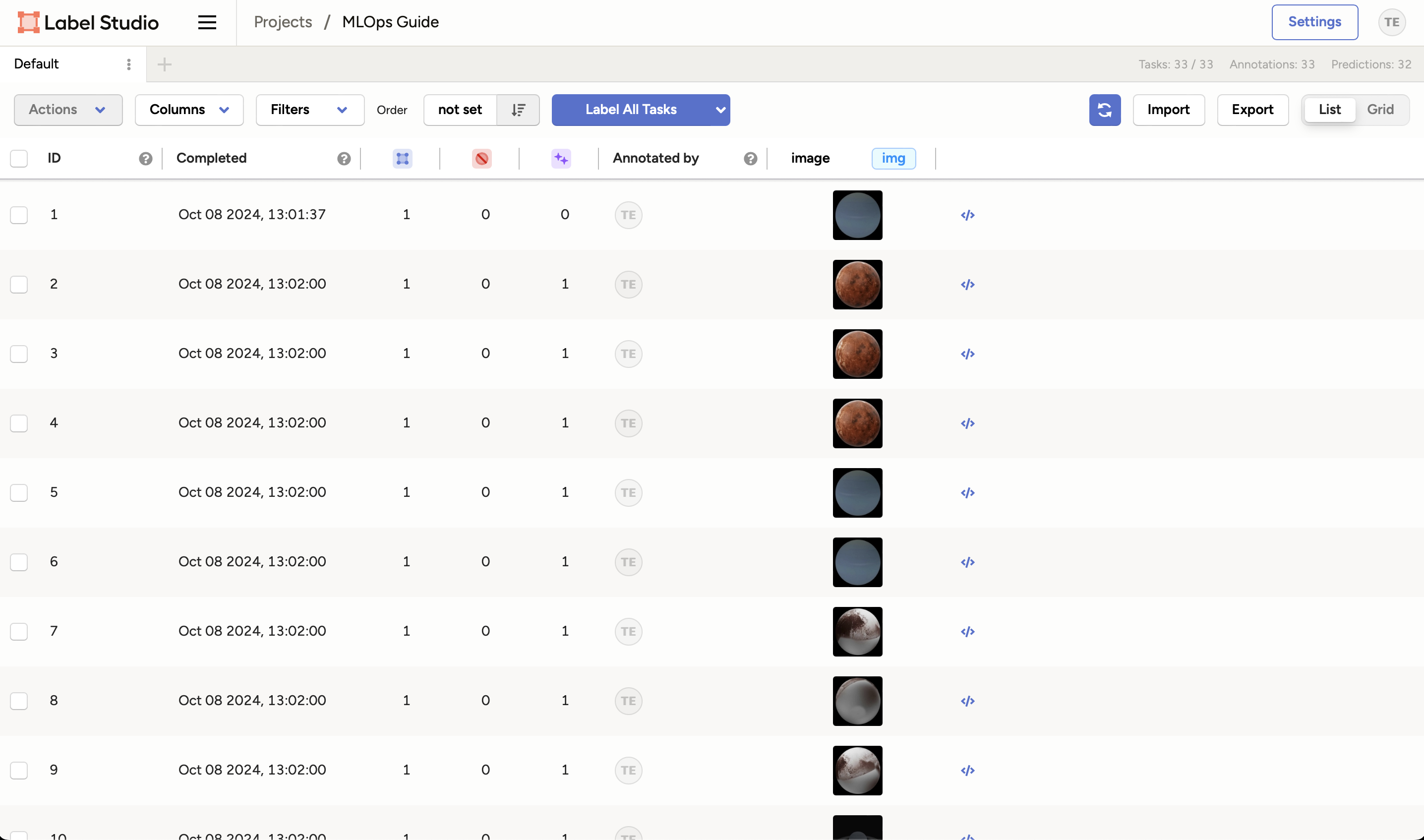
And that's it! You can view the annotations in the project view:
Warning
While AI-assisted labeling can significantly speed up the labeling process, it is important to be aware of its limitations. Human labelers might become overly reliant on the model's predictions and accept them without proper verification, especially when dealing with large datasets over extended periods. This can lead to inaccuracies in the labeled data.
To mitigate this risk, consider implementing cross-labeling, where multiple labelers annotate the same data and discrepancies are reviewed. This ensures higher accuracy and reliability of the labeled data.
Summary¶
Wow! You have successfully linked the model to Label Studio. You can now use the model to make predictions on the data you have in Label Studio to speed up the labeling process. In the next chapter, we will retrain the model using the new data we have labeled.
State of the labeling process¶
- Labeling of supplemental data can be done systematically and uniformly
- Labeling of supplemental data is accelerated with AI assistance
- Model needs to be retrained using higher-quality data